Omar Lozano
May 31, 2022
Foundations of Programming: Python
Assignment 07
https://github.com/omega609/IntroToProg-Python-Mod07
Pickling
Pickling is the process of converting a Python object into a byte stream to store it in a file and or database. It is a useful module to use when dealing with complicated data and allows the user to save a file without having to convert data into characters to save as a text file. Pickling is easy to use and does not require several lines of code as demonstrated in my program.
Creating the Script
In order to use pickling, the "pickle" module must first be imported, which was the first thing needed for this script along with defining my global variables. The variables include an empty list and the file the script will be write to (Figure 1).

Figure 1: import pickle module and declare global variables
Next, I create a function to save the data to a file with parameters representing the file and list of data that will be passed into the function. The binary file where I will store the list is opened using the open function. Just as we have seen before with the open function, the file and mode must be declared. However, instead of using the "w" mode, the "wb" mode is used to handle the file as binary. I also have to declare the data to "pickle" and the file where it will be stored. In this instance, the data is a list that will be created later by the user. Lastly, I close the file opened in this function (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Function to write a list object to a file in binary
I created a second function, "load_data". This function takes in the file as a parameter, opens the file and reads the pickled object from the file. The list is then created, unpickled and assigned to the local variable "file_data." The list is returned after the file is closed (figure 3).

Figure 3: Function to unpickle file
Structured Error Handling
There are two types of errors in Python: syntax and exceptions. Syntax errors are issues related to the written code that will cause a program to stop during execution. Exceptions are errors raised when the code is syntactically correct but an error resulted based off of the code and typically will not stop the execution of the program. I will discuss how I handled the ladder using a try and except statement.
For this assignment, I need a list that can be passed into the functions created in the previous section. Per our lecture, many errors occur when others are interacting with your code so I decided this would be the best place to show how the try except block is used to handle exceptions.
I start by asking the user to enter the make, model, and year of a car. A valid integer is required for the year, and a string is returned from the input. I attempt to convert the input to an integer. It is at this point that I use the try except to handle exceptions that may come up. If I am unable to convert the input to an integer, the except clause lets the user know they must enter a year as an integer. Likewise, the year must be greater than zero but less than 2022 or the user will also be informed to enter a year up to 2022. If an exception is not raised, "intYear" is assigned to the value entered and the except clause is skipped (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Try statement with except clause
Validating the Script
Validating this script works as intended requires two approaches: (1) through Pycharm and (2) using the Shell Operator.
Through Pycharm:
First, I ask the user to enter the make, model, and year and enter a valid make and model, and enter a string for the year. The exception is thrown when I enter a string for the year. I also enter an invalid integer and again I am prompted to enter a valid integer and finally the list of make, model and year are returned to the screen (Figure 5). Next, I go to Finder, Documents, _PythonClass, Assignment07, Assignment07test.dat and open the file and verify a file has been created with the byte stream (Figure 6).
Using the Shell Operator:
To validate the code works in the command shell, I copy the path and paste it to the command line. I run the script using different data from what was used in PyCharm, a string value for year of "seven", and capture the results of the code to demonstrate that the code works as intended (Figure 7). Finally, I use Finder again to locate the new Dat file created and validate the data entered has been pickled (Figure 8).
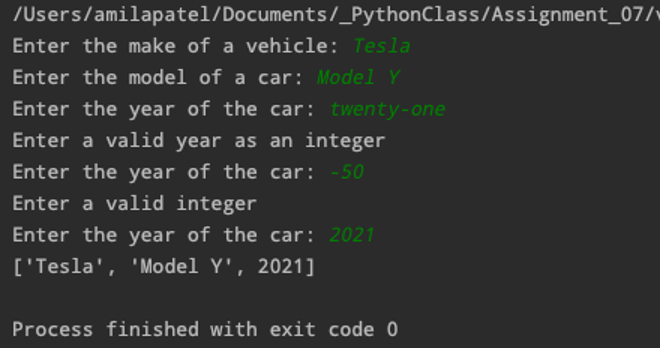
Figure 5: Exception "thrown" when string is entered

Figure 6: Dat file with binary protocol
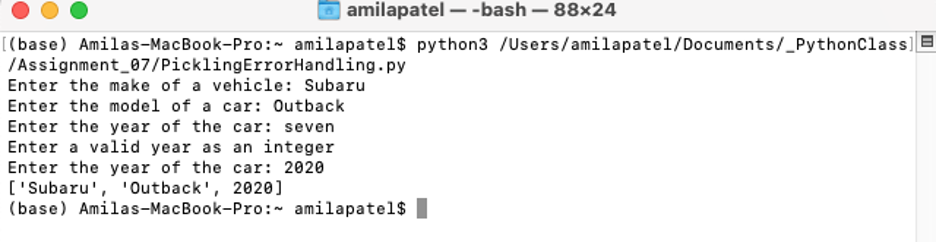
Figure 7: Exception thrown using shell and entering string for year

Figure 8: Dat File created using shell
Summary
For this assignment I was to demonstrate how pickling and structured error handling work which are two new tools that provide solutions to what would be otherwise difficult problems to solve.
Pickling is useful and does not require multiple lines of code making the storage of more complex data convenient. Structured error handling allows a program to continue while raising an exception and allows a user to provide a more meaningful error message to the user.